Introduction
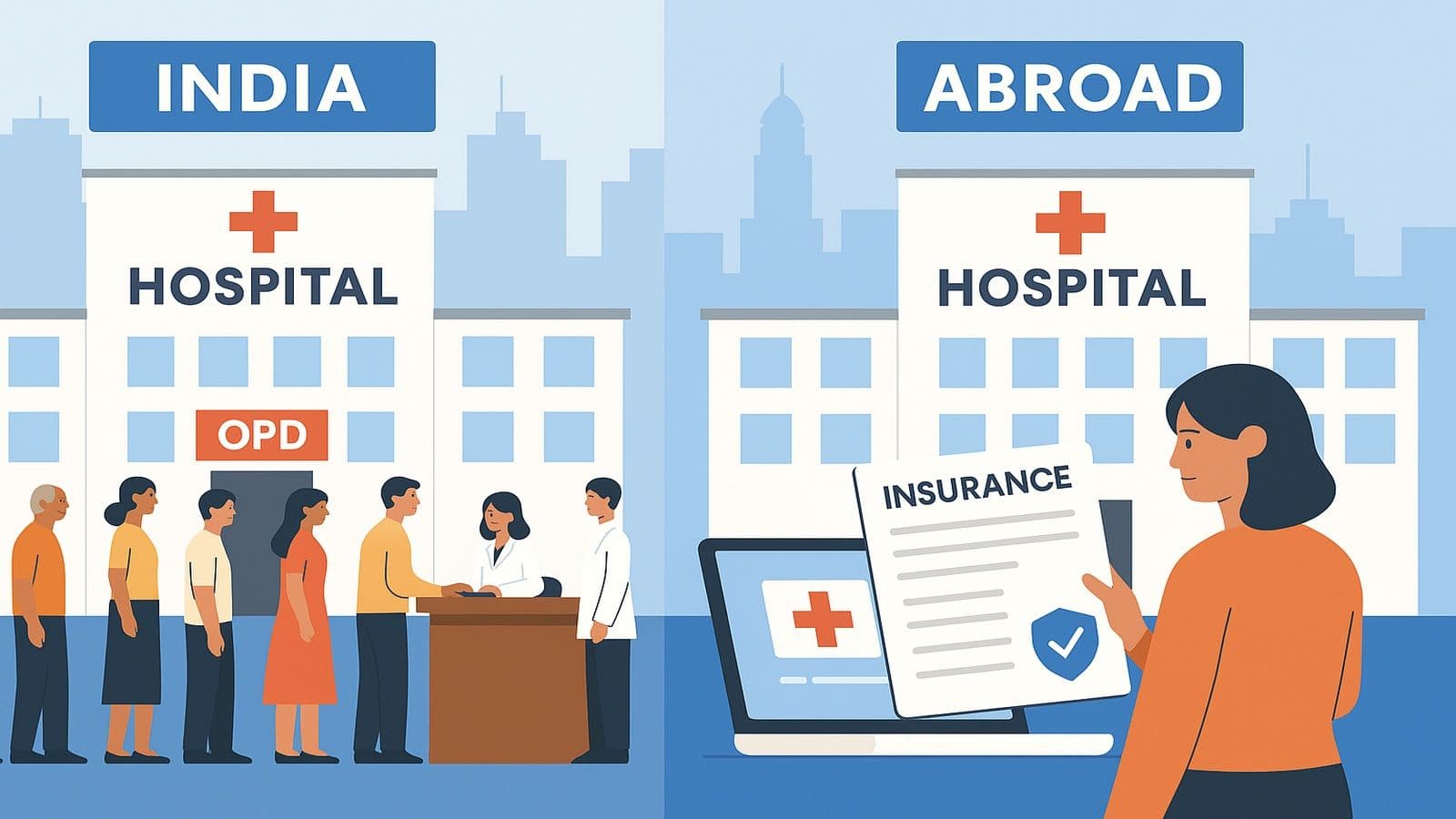
Picture two patients: one in Mumbai, another in Minneapolis. Both wake up with chest pain. The Mumbaikar grabs his phone, checks nearby healthcare facilities in India, and hopes the cardiology bill won’t empty the family savings. The Minneapolis patient wonders if his policy under the Affordable Care Act ACA covers today’s ER co-pay. That single morning captures “India vs United States” in a nutshell. But the story is bigger: Europe’s tax-funded clinics, Australia’s blended model, and Singapore’s tech-first strategy all add flavor to the global pot.
In this guide, we’ll unpack five clear contrasts between the India healthcare system and systems abroad. Whether you’re choosing a medical career path, eyeing a public-health MBA, or just curious, these real-world differences matter. And if you dream of fixing the health care system in India someday, read on—there’s plenty here to spark ideas.
While you read, you might also browse our post on how to become a Public Healthcare Administrator in India.
1. Insurance & Risk-Sharing
When you stack India vs United States, insurance is the first divide. In the U.S., the Affordable Care Act ACA nudged millions onto private plans, yet deductibles and paperwork still rule the day. Meanwhile, the India healthcare system finances roughly two-thirds of medical bills out-of-pocket. Ayushman Bharat is closing gaps, but employer coverage remains rare outside metros.
Abroad, especially in Western Europe, risk pools run through taxes. Citizens swipe a national card, see a doctor, and rarely see surprise bills. Indians, particularly in villages, still ask relatives for loans before surgery—a stark reminder that a health care system in India overhaul must start with smarter risk-sharing.
2. Infrastructure & Workforce
Urban India offers gleaming institutes, but step into a district hospital and the shortage of nurses, scanners, or even linen is obvious. Outbound medical tourists confirm that world-class healthcare facilities in India do exist—yet they’re concentrated in a handful of cities.
Compare that to Japan or Germany, where even small towns boast MRI suites. The best healthcare state in India—Kerala—achieved its status by prioritizing primary clinics and nurses. Its success hints that the India healthcare system can level up nationwide, provided other states copy Kerala’s playbook.
Curious about clinical degrees that feed this workforce? See our guide to MBBS, BAMS, BDS, BHMS Medical Courses.
3. Cost to Patients
Ask any traveller: surgery in Delhi might be cheaper than the same procedure’s co-pay in Dallas. Low labor costs, locally made implants, and price caps keep care within reach. That affordability turns India into a magnet for overseas patients—think knee replacements and eye surgeries.
Flip the script and you’ll see U.S. hospitals charging six-figure sums because of device mark-ups, administrative overhead, and defensive medicine. Even with the Affordable Care Act ACA, Americans often juggle medical credit cards. Yet cheap isn’t always cheerful; in the health care system in India, a rural family’s small bill can still be catastrophic if household income is tiny. Clearly, universal affordability is the next frontier.
4. Government Spending & Priorities
Europe budgets 8–12 % of GDP for health. The U.S. crosses 16 %. India hovers at 1.9 %. That ratio explains why the India healthcare system leans heavily on private clinics. More public resources would mean stocked pharmacies, functional ICUs, and timely ambulance services across states—not just in the best healthcare state in India.
Public-health think-tanks abroad also funnel cash into prevention: anti-smoking drives, mental-health hotlines, vaccination trackers. If the health care system in India followed suit, tackling diabetes and TB could cost far less than treating complications later.
5. Access & Equity
Imagine a pregnant woman in rural Rajasthan versus a mother-to-be in rural Sweden. One travels 50 km for an ultrasound; the other video-chats a midwife from home. Tele-medicine is growing fast in India, but bandwidth and awareness lag. Abroad, digital health is baked in.
Equity also swings on social safety nets. In the U.S., policy debates around the Affordable Care Act ACA decide if low-income residents keep their coverage. India faces a different equity puzzle: caste, language, and geography can all delay care. Bridging that divide will decide the future of healthcare facilities in India far more than adding shiny robots in city hospitals.
(Internal link) Students keen to be part of that solution can explore Top 14 Medical Courses After 12th for up-and-coming specialties.
Spotlight: Which Is the Best Healthcare State in India?
Data nerds debate hard, but Kerala usually wins the crown. High literacy, low infant mortality, and a dense network of primary centres push it ahead. Tamil Nadu and Himachal Pradesh trail closely. Yet even in Kerala, specialists note gaps in mental-health beds and geriatric care. The lesson? Celebrating the best healthcare state in India is great, but scaling its model nationwide matters more.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why does the U.S. rely so heavily on private insurance?
Historic employer-based coverage and political compromises birthed today’s insurance dominance, later formalised by the Affordable Care Act ACA.
2. Is care really cheaper in India?
Yes. The India healthcare system benefits from lower labor costs and price caps, though rural travel costs can add up.
3. Which indicators make Kerala the best healthcare state in India?
Low infant mortality, high immunisation, and community clinics pull Kerala ahead, showing what robust healthcare facilities in India can achieve.
4. How can tele-medicine bridge India’s rural gap?
Reliable internet plus trained nurses can beam city specialists into village clinics, lifting the overall health care system in India.
5. What role do preventive programs play abroad?
Governments fund lifestyle campaigns, screenings, and mental-health support—investments that reduce long-term strain on systems, something the India healthcare system can emulate.