The Difference between Modern Farming and Traditional Farming: A Complete Guide
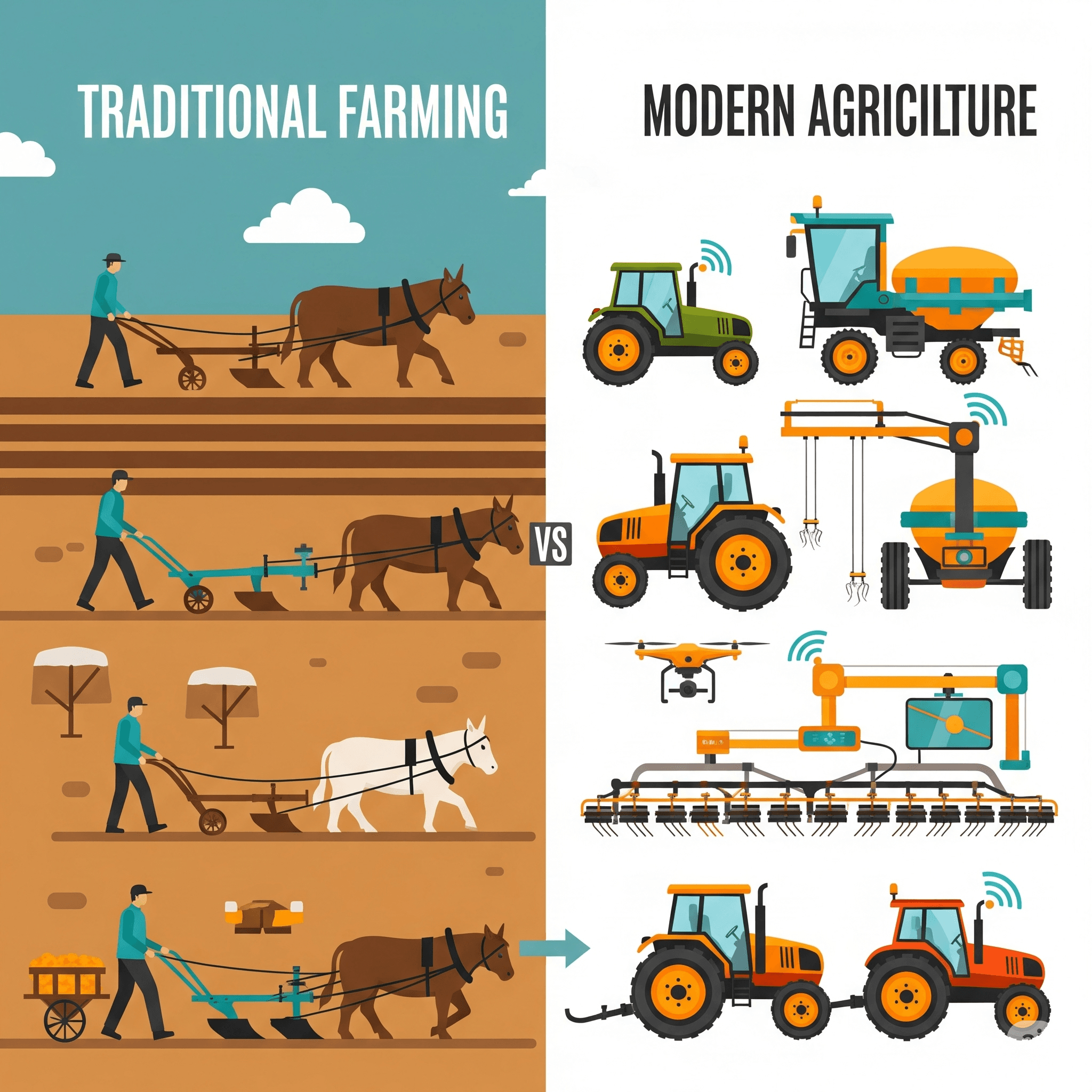
Agriculture has been a primary focus for every civilization. Current traditional farming relies on traditional methods for growing crops and managing land. Today, traditional farming is evolving into modern agriculture which is changing methods, strategies, tools, and outlooks. But, many consumers find it difficult to comprehend modern farming vs traditional farming. What is the difference between traditional farming vs. modern farming, and which is better for sustainability?
In this blog, we will discuss the difference between traditional farming and modern farming, the pros and cons of each, modern farming practices in India and current traditional farming practices in use today. Also do you know you can take agriculture as a career option? Want to know in depth about career paths, then talk with expert counsellors or even psychometric tests to examine your interest.
What is Traditional Farming?
Traditional farming is similar to ancient agricultural practices which, included the use of natural inputs such as animal manure, labor, and knowledge that has been shared locally through generations.
Characteristics of Traditional farming:
- Utilized organic manures and composts
- Manual implements, including sickles, plowing and hand-tools, transport using wooden carts.
- Rely on the nature of the climate for rainfall, rather than and efficient irrigation system.
- Crop rotations and mixed cropping are commonly used
- Low productivity, but ecologically balanced.
Here are some examples of traditional farming methods:
- Ploughing with oxen
- Composting and green manure
- Crop rotation
- Pest management, using natural supplies
- Native seeds.
These conventional agricultural practices still exist in rural India, particularly in Odisha, Uttarakhand, and parts of the Northeast. The focus is on balancing with nature and maintaining biodiversity.
What is Modern Farming?
Contemporary farming, or conventional agriculture, leverages current technologies and scientific methods to enhance agricultural production.
What are the hallmarks of contemporary agriculture?
Use of chemicals or fertilizers and pesticides
- Tractors, harvesters
- mechanized implements
- High-YieldingVariety (HYV) seeds
- Irrigation systems such as drip and sprinkler
- The use of biotechnology and GMOs
- Emphasizing monocropping
Some popular modern farming practices include:
- Multiple cropping
- Vertical farming
- Hydroponics and aquaponics
- Precision agriculture
- Mechanized farming
- Many institutions teach us these modern farming practices. For example, modern farming methods class 9 and curriculum about what is modern farming methods class 9 are often found in Indian school textbooks.
Traditional vs Modern farming – Pros and Cons
Pros of Traditional Farming:
- Environmentally sustainable
- Fostering biodiversity
- Maintaining soil health
- Less chemicals = healthier food
- Low input costs
Cons of Traditional Farming:
- Lower productivity
- Rainfall dependent
- Labour intensive
- Limited scalability
Pros of Modern Farming:
- Higher yield of crops
- Faster production cycle
- Less reliance on nature
- More mechanization, less human effort
- More suited for commercial agriculture
Cons of Modern Farming:
- Overuse of chemicals which destroy soil and health
- Costly equipment and inputs
- Environmental degradation
- Suspension of small farmers
Advantages of modern farming:
- Increased productivity, and food security
- Labor effort is reduced with mechanization
- Timely sowing and harvesting
- Precision farming with GPS and sensors
Disadvantages of modern farming:
- Depleting groundwater for irrigation
- Degrading soil with chemical use
- Dependence on machinery and fossil fuels
- Higher input costs
Conversely, advantages for traditional farming are:
- Environmental friendly and sustainable
- No chemical pollution
- Food produced is generally healthier
- Biodiversity preservation
Disadvantages for traditional farming are:
- Lower yield
- Time consuming by hand
- More susceptible to pests and climate change
Modern Farming Methods and Equipment
Modern farming methods are altering the world’s food systems. A few of the more common methods include:
- Precision agriculture: Uses GPS and sensors to monitor fields.
- Hydroponics: Soil-free farming with nutrient rich wastewater.
- Vertical farming: Shallow beds, with stacked farming surfaces
- Organic farming model: Incorporating modern approaches with organic inputs.
- Smart irrigation: Automated irrigation systems to conserve water, and increase yield.
Traditional Agriculture in India
India has a vast and deep tradition of agriculture. The uses of cow dung to the ancient ways of farming were rooted in a sustainable way of traditional Indian agriculture.
Examples of Traditional Ways of Agriculture in India:
- Zai pits in Maharashtra
- Bamboo drip irrigation in Meghalaya
- Step farming in Himachal and Uttarakhand
Even today traditional ways of agriculture in India are promoted for organic farming and sustainable lifestyles.
Traditional Farming vs Modern Farming in India
For centuries agriculture has been the mainstay for many rural sectors in India. Traditional farming was based on climate and seasonal patterns, livestock (cattle) usage and organic practices. Farmers relied on traditional agricultural tools such as the plough, sickle, bullocks, equipment made by hand that had all been handed down from previous generations.
Traditional agricultural practices due to their place while tied with the climate were based on environmental realities. Crops were grown based on climate and local soil besides speaking for soil and water conservation and also for its long term fertility. Although the crops had limited yields, weather dependent (natural rainfall).
In relation, modern farming in India has undergone a complete alteration since the last few decades following Independence. Unlike traditional farming, the new growing and farming technology is considerably suprabundantly integrated in agriculture. Modern farming in India includes hybridization of crops, chemical fertilizers, genetically modified crops, mechanization such as tractors and harvesters, and advanced irrigation methods like drip or sprinkler systems.
There are good reasons to know the difference between traditional farming and modern farming!
Knowing the difference between traditional farming and modern farming in points will help us decide the way forward.
Together with climate change concerns, traditional agriculture has become a global comparative advantage. Government and NGO efforts to promote hybrid models are very reasonable, combining modern science with traditional wisdom, to promote natural farming, organic farming, low-input sustainable agriculture.