Have you heard of the word something as an entrepreneur8? You may have but the real question is what does that mean? What is entrepreneurship? Because every other person calls himself/herself an entrepreneur nowadays. Is it some kind of trend? Well, it actually is but in the aspect of money. What does that mean? Well in simple words an entrepreneur is a person who starts, builds, and manages a business. An entrepreneur usually identifies as a risk taker having innovative solutions and turning ideas into successful ventures. If you also want to build up a business or start a startup then you can start with counselling from experts or even take a psychometric test to test your intelligence so you can start from scratch.
For starting a business or a startup you need to have the right amount of knowledge and this blog will guide you through it. While most are familiar with classic entrepreneurs, such as tech founders (e.g. Steve Jobs, Elon Musk), or small business owners, there are many less-known or underappreciated types of entrepreneurs that are important in today's economy and society. Here are some examples of types of entrepreneurs you may not have known about or thought of. This blog explains the types of entrepreneurship in the simplest way.
Types of entrepreneurship.
You may wonder how many types of entrepreneurship there are. While there are ‘n’ number of entrepreneurs we cannot exactly decide how many types of entrepreneurs are currently working. For a start let's see what are the 4 types of entrepreneurship.
What are the 4 types of entrepreneurship?
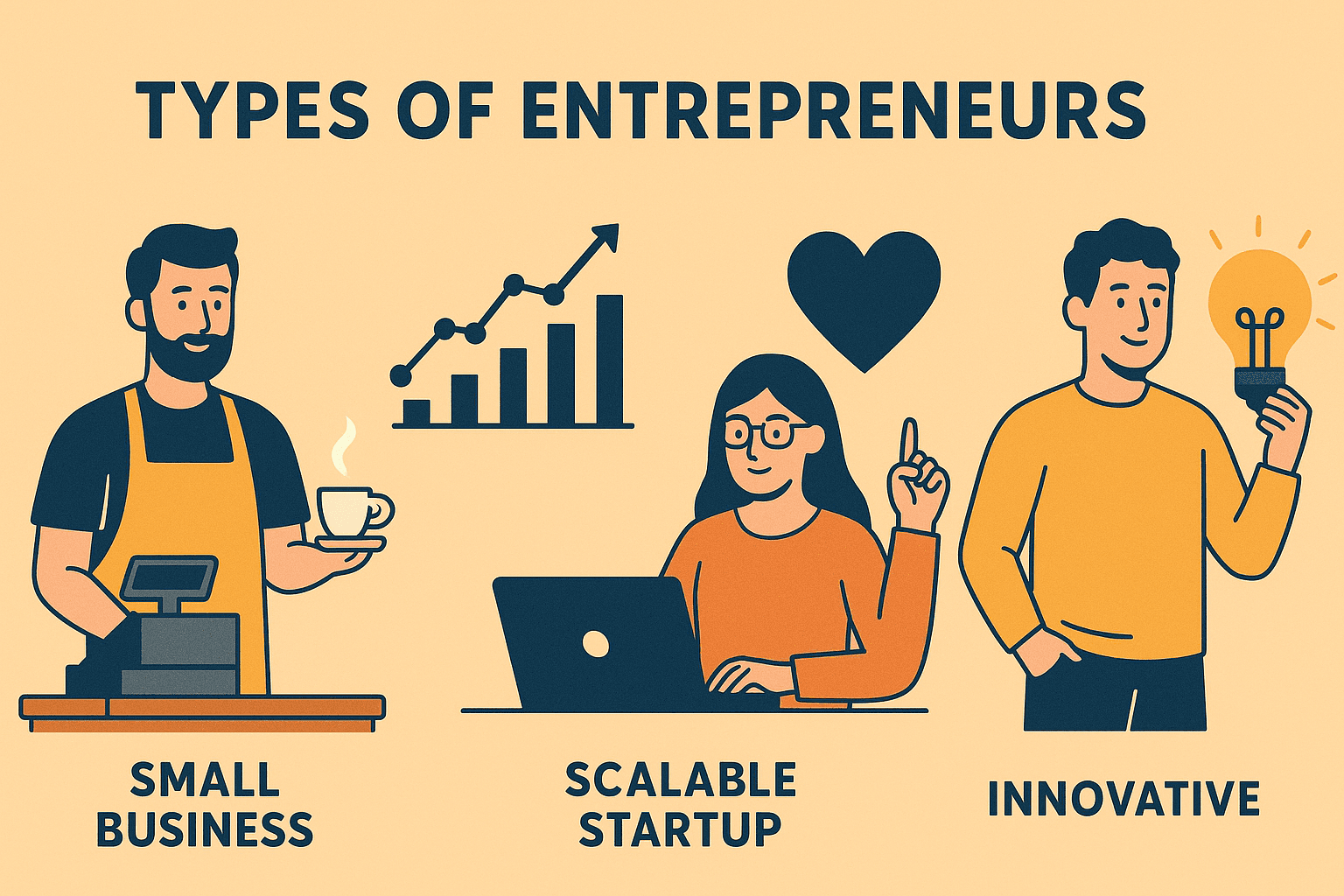
1. Small Business Entrepreneur or entrepreneurship
Have you heard when people say “he is a business entrepreneur”. This is exactly what they mean and below listed are the areas that are covered in small business entrepreneurship.
- What is it: Starting a business with the intention of providing income for your living (not with the intention of becoming a billionaire).
- Examples: Grocery store, bakery, salon, clothing boutique.
- Goal: Earn a reasonable living, support the family, and be self-employed.
2. Scalable Startup Entrepreneurship
- What is it: Starting a startup with the aim of growing big, very fast.
- Examples: Tech startups like Facebook, Zomato, and Paytm.
- Goal: The aim of Scalable Startup Entrepreneurs is to get investment, scale the business globally, and disrupt the industry.
3. Large Company Entrepreneurship
- What is it: Innovating within an existing company.
- Examples: Google launching services, Apple releasing the Apple Watch.
- Goal: Stay competitive by innovating and developing new products in response to trends.
4. Social Entrepreneurship
- What is it: Creating businesses that help solve social problems or environmental concerns.
- Examples: Nonprofit companies, clean energy startups, non-governmental organizations.
- Goal: To generate social impact rather than maximizing profit.
Above listed were the main and well-known types of entrepreneurship. Now we are looking into a more diverse area covering a wide range.
Explain different types of entrepreneurship.
Freelance Entrepreneurship / Solopreneurship
Any individual can essentially build a freelance business in today's economy, especially if you live in a country like the U.S. where startup costs are low. Freelancers in essence are really just exchanging time for money, and having flexibility and independence.
Solopreneurs are predominantly individuals, but can at times outsource a lot of what they do and still consider themselves the only employee of the company. They are the CEO, marketer, and customer support person all in one.
Social Entrepreneurship
Social entrepreneurs create social ventures that help society, often focused on issues like poverty, education, or women empowerment.
Social businesses operate with impact over income, often with an associated nonprofit organization, or community-based business model.
Some of the more popular social entrepreneurs are Urvashi Sahni, Anshu Gupta, and Bill Drayton.
Speculative Entrepreneurship
Speculative entrepreneurs generally come to the table with money to invest, but not necessarily their own. This type of entrepreneur typically seeks out business opportunities that require a significant, large amount of capital upfront and a high level of risk to start. Financial backers, like speculative entrepreneurs, expect to see a high return of investment after the first few years of business, but want someone else to do it on their behalf.
Hustler Entrepreneur
Hustler entrepreneurs exhibit tremendous grit, determination, and self-motivation. They usually start out small (really small) with limited resources and are typically ultimately broke. These types of entrepreneurs will always be successful in the highly competitive world of business because they are hard-working, networking, and persistent. Hustler entrepreneurs often don’t wait for opportunities to come to them; they create the opportunities.
Franchise Entrepreneur
So instead of starting from scratch, these types of entrepreneurs buy into a franchise model like McDonald's or Domino’s. As franchise entrepreneurs, they have a ready-made brand, training, system, and support. If you are truly looking for an established business with a known entity, the amount of franchise startup will depend on the brand and industry and can vary from $10,000 to $5 million.
Innovative Entrepreneurs
These entrepreneurs are different because they develop completely new ideas, products, or services that radically change how we live or do business. These are the "wild" thinkers - the visionaries such as Steve Jobs - they play on the edge of innovation and creativity.
Imitator Entrepreneurs
Imitator entrepreneurs take the work of others and improve on it or it has inspired them to improve their ideas or products. Imitating does not mean inventing from scratch, it can just mean adding some features or usability, to enter a market that no one else is serving by improving on what others have done.
Scalable Startup Entrepreneurs
These entrepreneurs want to build businesses with a high growth potential. Their business is usually based on disruptive ideas that have unlimited scalability and usually technology-based. The founders of Facebook or Instagram started off with an idea, and as most of us know, quickly turned them into global companies.
Environmental Entrepreneurs (Ecopreneurs)
Also known as green entrepreneurs, these entrepreneurs build companies primarily focused on solving environmental issues. Their goal is to have a positive impact on the planet while making money. They tend to focus on sustainable business, clean energy, zero waste, Eco-innovation, etc.
Researcher Entrepreneurs
Researcher entrepreneurs are systematic and accurate. They do not launch anything unless they have collected market and product research. They strive to make informed decisions, minimize risk, and ground their process in plans with realistic treatment for the other steps. Researcher entrepreneurs believe in the idea that conducting appropriate research lowers the chance of failure, and they are usually right.
Forms of entrepreneurship.
While there are many different types of entrepreneurship that are known and unknown to people there is also an area that comes under forms of entrepreneurship. These forms of entrepreneurship are slightly different and kind of contrasting from the basic types but the central idea remains the same.
1. Intrapreneurs
- Who they are: Employees within a company who behave like entrepreneurs — innovating, launching new ideas, or starting projects as if the company was their own.
- Example: The team at Google that developed Gmail.
2. Ecopreneurs
- Who they are: Entrepreneurs focused on sustainable and environmentally friendly ventures.
- Why they're unique: They prioritize the planet over profit — or try to balance both.
- Example: Founders of companies that turn waste into usable products or carbon-negative startups.
3. Faithpreneurs
- Who they are: Entrepreneurs who build businesses around faith-based values or serve faith communities.
- Unique twist: Their business model may blend spiritual leadership with economic growth.
4. Technopreneurs
- Who they are: Tech-savvy entrepreneurs who use cutting-edge technology to create new products or disrupt traditional industries.
- Distinct focus: Deep integration of innovation and R&D.
5. Seniorpreneurs
- Who they are: Older adults (often retirees) who start businesses later in life.
- Surprising fact: They often outperform younger entrepreneurs in long-term business success due to experience.
6. Social Entrepreneurs
- Who they are: People who launch ventures to solve social problems (like poverty, education gaps, or access to clean water).
- Different goal: Impact > Income.
- Example: Muhammad Yunus (Grameen Bank).
7. Contentpreneurs
- Who they are: Creators who turn content creation (YouTube, TikTok, blogs, etc.) into a business.
- Why it's different: Low capital, high scalability via personal branding.
8. TravelPreneurs / Digital Nomad Entrepreneurs
- Who they are: People who run location-independent businesses while traveling the world.
- Modern lifestyle: Leveraging online income to fund global travel.
9. Designpreneurs
- Who they are: Designers who turn their creative skills into entrepreneurial ventures — often in fashion, UI/UX, or product design.
- Strength: Marrying creativity with commerce.
10. Policypreneurs
- Who they are: Innovators in the public policy or governance space who "disrupt" policy-making with tech or new models (often within NGOs or political organizations).
- Emerging field: Especially relevant in areas needing reform (healthcare, education, etc.).
Done reading now you must be eager to be an entrepreneur as well, and let me tell you, you definitely can be and will be an entrepreneur. Whether you are in school, don't let your creative thinking stop from school to startup you can be an entrepreneur too.